
Failures which occur that can be left or maintained in an unrepaired condition, and do not place the system out of service, are not considered failures under this definition. For complex, repairable systems, failures are considered to be those out of design conditions which place the system out of service and into a state for repair.
The definition of MTBF depends on the definition of what is considered a failure. The term is used for repairable systems, while mean time to failure ( MTTF) denotes the expected time to failure for a non-repairable system. MTBF can be calculated as the arithmetic mean (average) time between failures of a system. Mean time between failures ( MTBF) is the predicted elapsed time between inherent failures of a mechanical or electronic system, during normal system operation. There are also options to easily re-run stability analysis after changing data or control limit calculations.Predicted elapsed time between inherent failures of a system during operation
#Minitab calculator update#
Once you create a control chart using QI Macros, you can easily update the control limits using the QI Macros Chart Tools menu. determine when you have had a process change and need to recalculate your control limits.įREE QI Macros 30-Day Trial QI Macros Also Makes it Easy to Update Control Limit Calculations.highlight unstable points and trends in red.analyze your data and select the right control chart (and formulas) for you.QI Macros built in code is smart enough to: QI Macros calculations are tested and accurate. Just select your data and QI Macros does all of the calculations and draws the control chart for you. QI Macros is an easy to use add-in for Excel that installs a new tab on Excel's toolbar.
#Minitab calculator software#
Instead, use proven software like QI Macros Add-in for Excel
#Minitab calculator manual#
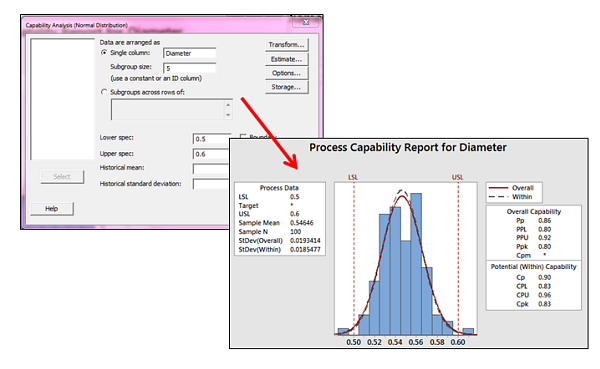
You'll probably make mistakes and aggravate customers.Software! You can try and calculate sigma and the control limits yourself, but. Montgomery * The secret formula to ignoring all other formulas. * "Introduction to Statistical Quality Control," Douglas C. Here are some examples of control limit formulas: There are seven main types of control charts (c, p, u, np, individual moving range XmR, XbarR and XbarS.) Plus there are many more variations for special circumstances. The formula for sigma depends on the type of data you have:Įach type of data has its own distinct formula for sigma and, therefore, its own type of control chart. Why are there so many formulas for sigma? ± 2 sigma and ± 3 sigma from the center line.
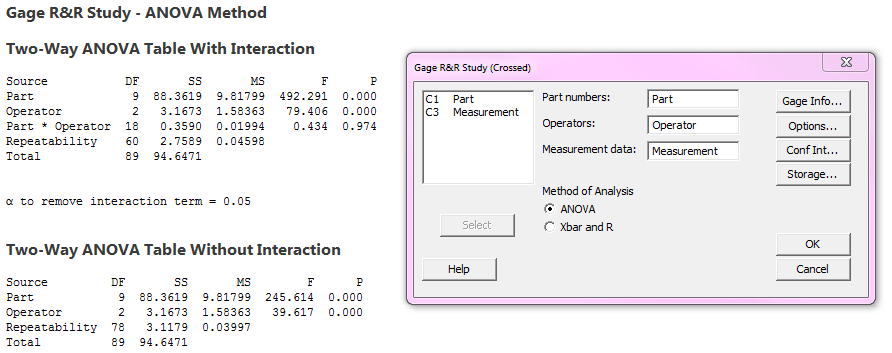
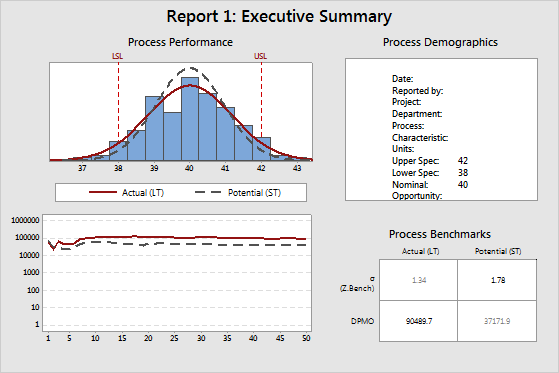
The formula for sigma varies depending on the type of data you have. The Center Line equals either the average or median of your data. The secret formula that helps you ignore the rest!


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
